Oral cancer is the most common cancer in India, causing 145,000 deaths annually. “The management of oral cancers is complex, due to the functional and aesthetic implications in this region.”
ORAL CAVITY:
There are seven oral cavity subsites. They are tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, hard palate, alveolus, retromolar trigone and soft palate. It can also affect the salivary glands.
RISK FACTORS:
Tobacco and alcohol intake are the main risk factors for the development of oral cancers. Betel nut (supari) chewing is also known to cause cancer. Other factors include HPV infection, UV exposure, chronic trauma, irritating dentures are poor oral hygiene.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION:
Most cancers are preceded by pre-malignant lesions, like restriction in mouth opening, persistent red or white patches in mouth. The most common presentation is a non-healing wound. Patients may also prevent with mobile teeth, bleeding, pain or numbness in the mouth or face or ill-fitting dentures. A non-healing extraction socket – 6 weeks should raise suspicious. Any lesion which fails to resolve in 2-3 weeks should be investigated.
ORAL SCREENING:
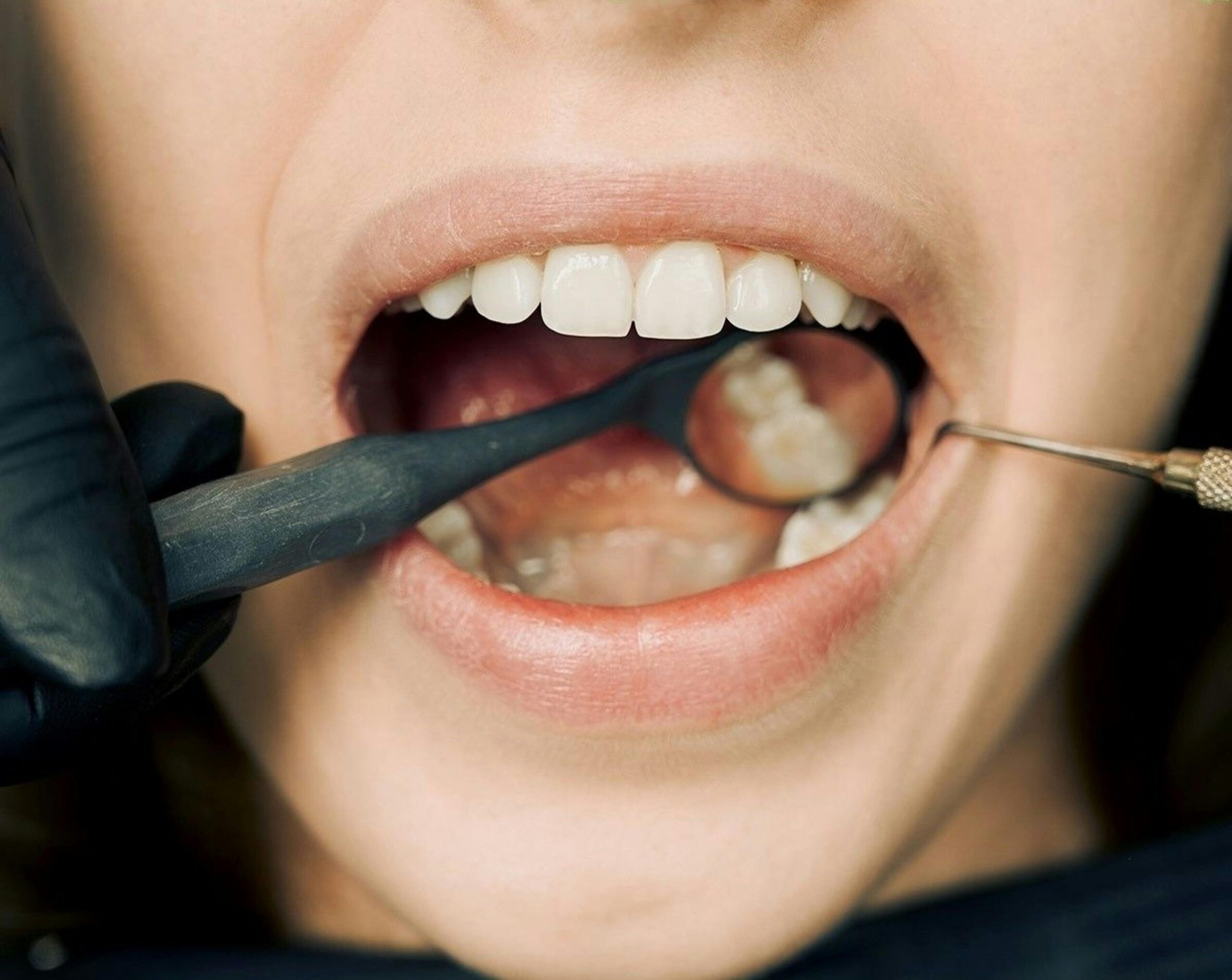
Oral cancers can be identified at an early stage by clinical examination. However, more than 50% report for treatment with an advanced tumor. Oral screening includes visual inspection of the subsites of the oral cavity. It also includes palpating the regional lymph nodes.
EARLY DIAGNOSIS:
Early diagnosis is essential to decrease morbidity and mortality. In early stages, the lesion may be flat or elevated and may be minimally palpable. Some cancers may be asymptomatic. Examination by dentist/doctor is an important means for early identification and diagnosis.
MANAGEMENT:
- Surgery is the primary modality of treatment. Resection surgery includes removal of tumor and the affected lymph nodes. Reconstruction surgery essentially involves minimizing the morbidity of the resection.
- Radiation therapy is often indicated in advanced cancers and involves the use of ionizing radiation.
- Chemotherapy is often added to radiation in certain cases of aggressive tumors and includes injections that are toxic to cancer cells.
FOLLOW-UP:
Every patient requires long-term follow up aimed at not only looking out for recurrences or new cancers, but addressing the morbidity from treatment like speech and swallow issues, preservation of teeth and restoration of missing teeth.